Green Buildings
Sustainability
Sustainability can be defined as the ability to meet the needs the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
Green building is often used as a synonym for sustainable Construction and high - performance buildings.
For what should be apply
- Residential Villas.
- Residential and commercial buildings.
- Apartments - Workers' housing - Student housing
- Commercial
- Hotel Facilities - Hotels
- Laboratories - Offices - Resorts - Restaurants
- Public buildings.
- Banks and expenses - Theaters and cinemas - Educational buildings - Governmental buildings - Buildings and health facilities - Historical and heritage buildings.
- Museums, petrol stations, post offices, retail stores, shopping centers , Houses of worship.
(1) Sustainable Sites
(1-A) Site Assessment
A site assessment assesses site conditions before design to evaluate sustainable options and inform related decisions about site design.
A site assessment is part of the integrative process that helps to incorporate the assets of the site and its historical contexts.
(1-A-1) Site Assessment - Topography
Contour mapping, unique topographic features, slope stability risks.
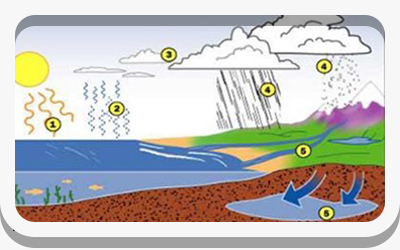
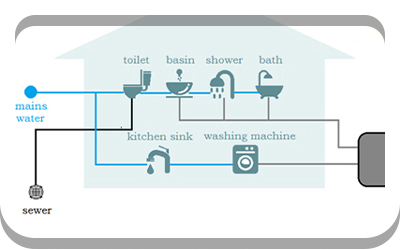
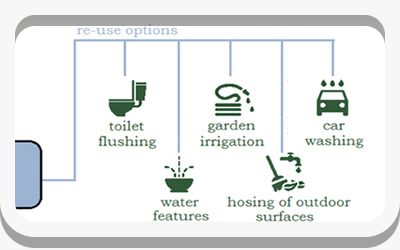
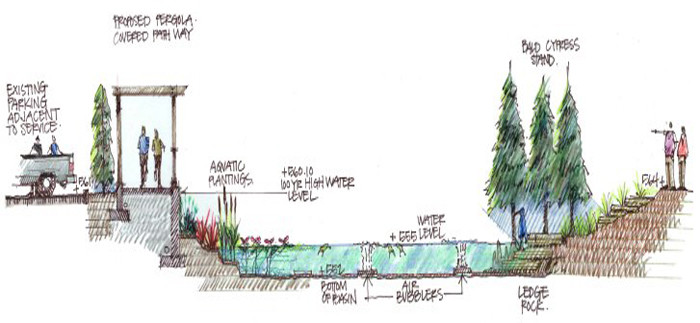
(1-A-2) Site Assessment - Hydrology
Flood hazard areas, delineated wetlands, lakes, streams, shorelines, rainwater collection and reuse opportunities.
The hydrologic cycle keeps the Earth's fresh water supply on the move.
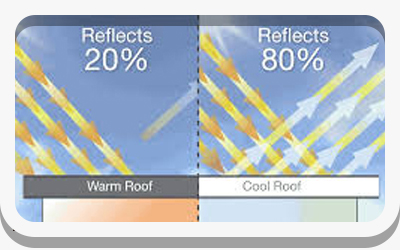
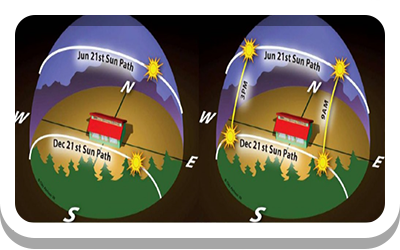
(1-A-3) Site Assessment - Climate
Solar exposure, heat island effect potential, seasonal sun angles, prevailing winds, monthly precipitation and temperature ranges.

(1-A-4) Site Assessment - Vegetation
Primary vegetation types, greenfield area, significant tree mapping, threatened or endangered species, unique habitat, invasive plant species.
(1-A-5) Site Assessment - Soils
Prime farmland, healthy soils. Thorough investigation and assessment of ground conditions and stability to determine whether a site is suitable for building on, and the type and size of foundations that will be required.


(1-A-6) Site Assessment - Human Use
Views, adjacent transportation infrastructure, construction materials with existing recycle or reuse potential.
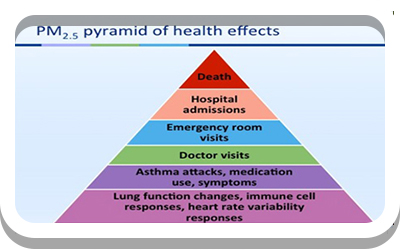
(1-A-7) Site Assessment – Human Health Effects
Proximity of vulnerable populations, adjacent physical activity opportunities, proximity to major sources of air pollution.